Why Do Piles Bleed? Understanding the Root Cause
Piles (hemorrhoids) are a common condition affecting people of all ages. While pain, itching, and discomfort are frequent complaints, bleeding is often the symptom that alarms patients the most. Seeing blood during or after a bowel movement can be frightening, but understanding why piles bleed helps with appropriate self-care and timely treatment.
What Are Piles, and Why Do They Bleed?
Piles are swollen and inflamed blood vessels in the lower rectum and anus. Increased pressure causes these vessels to enlarge and, depending on their location, they are classified as internal or external. The delicate lining of the rectum and irritation of the anal skin make these vessels prone to bleeding.
1. Internal Piles
Internal piles lie inside the rectum and have fewer pain receptors, so they may not hurt but are more likely to bleed. The rectal lining is delicate and can tear during passage of stool, causing bright red blood.
2. External Piles
External piles develop around the anal opening. They may bleed if a clot forms and ruptures (thrombosed pile) or if the skin is irritated by rubbing or wiping.
Main Reasons Why Piles Bleed
Bleeding from piles is commonly due to pressure, friction, and inflammation. Common causes include:
- Hard stool and constipation: Straining to pass hard stools stretches and tears fragile vessels, causing bleeding.
- Excessive straining: Repeated straining weakens vein walls and promotes bulging and rupture.
- Chronic diarrhea: Frequent loose stools irritate the anal lining and can cause bleeding.
- Prolonged toilet sitting: Long periods on the toilet increase blood flow to the rectal area, promoting swelling and bleeding.
- Pregnancy and childbirth: Increased abdominal pressure, hormonal changes, and straining during delivery raise the risk of bleeding hemorrhoids.
- Obesity: Extra pelvic pressure from excess weight predisposes to swollen veins that can bleed.
- Heavy lifting: Improper heavy lifting suddenly raises intra-abdominal pressure, which can precipitate bleeding.
- Rough wiping or over-cleaning: Abrasive toilet paper or vigorous cleaning can irritate the area and cause bleeding, especially with external piles.
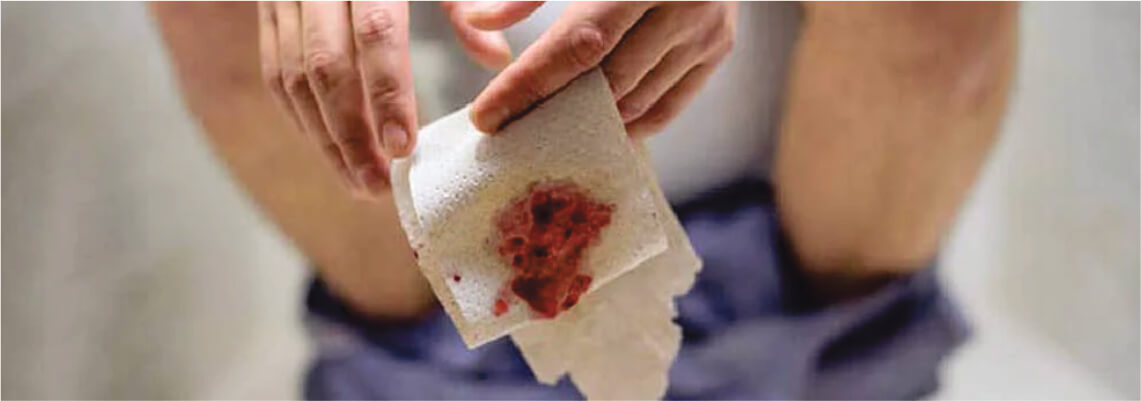
How Much Bleeding Is Normal?
Typical hemorrhoidal bleeding is bright red and usually minimal—seen on toilet paper, in the bowl, or coating stool. However, continuous or heavy bleeding is not normal. Seek medical attention if you notice:
- Large amounts of blood
- Bleeding that lasts several days
- Dizziness, weakness, or fainting
- Dark or tarry stools
Are Bleeding Piles Dangerous?
Bleeding piles are usually not life-threatening, but untreated or recurrent bleeding can cause complications such as anemia, severe pain from thrombosis, infection, or prolapse that worsens over time. Early evaluation prevents complications and speeds recovery.
When to See a Specialist
If bleeding is heavy, persistent, or accompanied by weakness or dark stools, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Evaluation helps rule out other causes of rectal bleeding and guides appropriate treatment.
Final Thoughts
Bleeding from piles is commonly related to constipation, straining, or increased pressure on the rectal veins. Many cases respond to lifestyle changes (fiber, hydration, avoiding straining), topical care, and medical management. For persistent or severe symptoms, specialist assessment is advised.
For expert diagnosis and treatment, consult Dr Sandip at Pelvinic Clinic for personalised care and effective management of bleeding piles.